Top Gear Pump Types Explained for Efficient Fluid Transfer?
Gear pumps are vital in the world of fluid transfer. They provide efficient, reliable movement of various fluids in numerous applications. Understanding these pumps is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
The gear pump operates by using meshing gears to create a void that draws fluids in and pushes them out. This method ensures a steady flow, ideal for many industries. Yet, not all gear pumps are the same. They vary in design and application needs. Knowledge of these differences affects your choices.
However, it’s crucial to be aware of their limitations. Gear pumps can struggle with certain viscous fluids. Choosing the wrong pump can lead to inefficiency. It’s a learning process that highlights the need for careful selection and maintenance. Embracing this knowledge can lead to better efficiency in fluid transfer systems.

Types of Pumps Used in Fluid Transfer Applications
Fluid transfer applications require reliable pumps to move liquids efficiently. Various pump types serve different needs. Positive displacement pumps are popular for their ability to deliver a constant flow rate. These pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and pushing it through the outlet. You’ll find them in applications where precise flow control is essential. They can handle thick fluids well.
Centrifugal pumps are another common choice. They use rotational energy to move fluids. This type is ideal for large volumes and low-viscosity liquids. However, they can struggle with thick or viscous substances, leading to inefficiency. Knowing the system's requirements helps in choosing the right pump.
Not every application needs the most powerful pump available. Sometimes, a smaller, less efficient option could be more suitable. It's crucial to evaluate the entire system. Consider pressure, temperature, and fluid properties. Optimization is often necessary for effective fluid transfer. Balancing efficiency and operational needs can lead to unexpected challenges in performance.
Principles of Operation for Different Pump Types
When it comes to fluid transfer, understanding pump types is crucial. Different pumps operate on unique principles, influencing efficiency and suitability. Centrifugal pumps use rotational energy to move fluids. They are ideal for large volume transfers. Yet, their efficiency can drop with high-viscosity liquids. This limitation is important for industries dealing with thick substances.
Positive displacement pumps are another category. They work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge. This method ensures a constant flow rate, regardless of pressure changes. However, these pumps can cause damage if operated against closed valves. A study by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers indicates that about 30% of pump failures result from improper application. This emphasizes the need for careful selection.
For specific applications, gear pumps are notable. These pumps are efficient for precisely metering fluids. However, they can be sensitive to temperature changes, which may alter fluid viscosity. According to the Hydraulic Institute, optimized pump selection can improve system efficiency by over 20%. This statistic is compelling, yet the oversight of the pump's operational environment can lead to underperformance in many setups.
Top Gear Pump Types Explained for Efficient Fluid Transfer
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency of various pump types used for fluid transfer, measured in liters per minute (L/min). The data reflects the operational capabilities of centrifugal, gear, diaphragm, and peristaltic pumps, showcasing their specific strengths in different applications.
Efficiency Considerations for Pump Selection

Choosing the right pump is crucial for efficient fluid transfer. Efficiency considerations play a significant role in the selection process. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, pump efficiency in industrial applications can range from 40% to 90%. This variation impacts operational costs significantly. For instance, a pump operating at 60% efficiency can incur up to 30% higher energy costs compared to one functioning at 85% efficiency.
Flow rate, pressure requirements, and viscosity of the fluid all influence pump selection. More complex fluids may require specialized pumps, which can often lead to higher maintenance costs. It's essential to consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price. A recent study showed that optimizing pump systems can save energy costs by up to 20%. However, many industries overlook these potential savings.
Moreover, the installation environment matters. Ambient temperature and surrounding conditions affect pump performance. In some cases, pumps may fail under extremes, resulting in downtime and additional losses. One study indicated that 25% of pumps experience unexpected failures, often due to poor selection and installation practices. Reflecting on these factors can improve efficiency and reduce waste in fluid transfer systems.
Applications of Various Pump Types in Industry
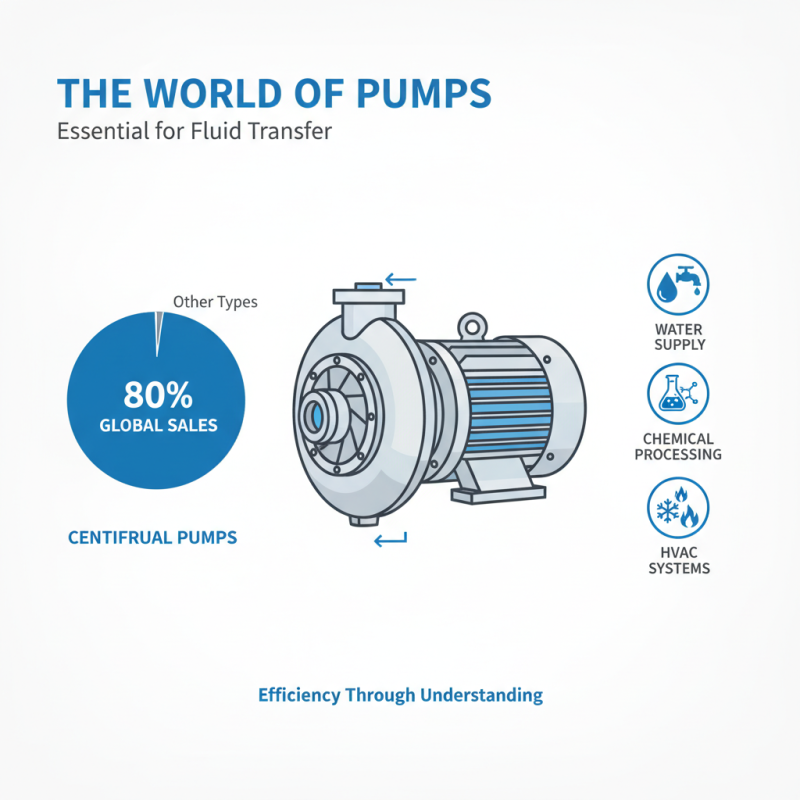
Pumps are vital in various industries. They facilitate fluid transfer for different applications. Understanding their types is essential for efficiency. Centrifugal pumps dominate the market. They account for approximately 80% of the global pump sales. These pumps are widely used in water supply, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Positive displacement pumps are another category. They move fixed volumes of fluid, making them ideal for applications needing exact flow rates. The oil and gas sector relies heavily on these pumps. According to industry reports, nearly 25% of their operational costs are linked to pumping equipment. This data emphasizes the importance of selecting the right pump type.
Manufacturers face challenges in pump efficiency and maintenance. Many pumps operate below their optimal performance level. This inefficiency can lead to increased energy consumption and downtime. It's crucial for professionals to regularly assess and optimize pump performance. Identifying the right application can save costs and enhance productivity.
Maintenance Practices for Optimal Pump Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for pump performance and longevity. According to a study by the Fluid Handling Institute, maintenance neglect can lead to a 30% decrease in pump efficiency over time. Monitoring key components like seals, bearings, and impellers can prevent costly failures. Often, operators overlook the importance of lubrication. Lack of proper lubrication can result in increased friction and wear. This can shorten pump life, leading to unexpected downtime.
Another critical aspect is performance testing. Regular tests help identify potential issues early. The Hydraulic Institute states that 20% of pumps in operation are running at suboptimal performance levels. Visual inspections and vibration analysis are effective methods for early detection. However, these checks are often skipped, leading to bigger problems down the line.
Training for operators is essential. Well-informed staff can detect changes in pump behavior more readily. Continuous education ensures that maintenance practices stay up-to-date. Yet, many facilities lack ongoing training programs. Ignoring this can lead to a skills gap. Proper maintenance is a combination of knowledge, attention to detail, and consistent practice. It requires commitment from everyone involved.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Gear Pump for Your Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Gear Pump for Your Application Needs
-

Top 5 Diesel Transfer Tanks with Pump for Efficient Fuel Management
-

How to Select the Right Chemical Pump for Your Industrial Needs
-

Progressive Cavity Pumps Exposed: A Comprehensive Comparison of Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
-

Understanding the Benefits of a Diesel Transfer Tank with Pump for Efficient Fuel Management